Good retirement income planning involves adjusting to circumstances and evaluating innovative products. Consider an FIA to manage downside risk.
I have spent my career looking for new ways for retirees to create income — particularly safe, lifetime income — and at the same time meet their objectives for legacy, inflation protection, liquidity and risk management.
I think about results, not specific products, so although annuity payments have been at the core of my research and approach, I have incorporated other types of income sources into my Go2Income planning method, too. The latest is called a fixed index annuity (FIA), which has become a trillion-dollar industry because it protects your investment during bad markets while getting higher returns than fixed-income portfolios in most scenarios.
It’s our job at Go2Income to do the analysis for investors like you.

What is a fixed index annuity?
Just like other types of annuities, you purchase an FIA from an insurance company. It offers the tax-deferral benefits of annuities and, similar to new forms of investment vehicles like buffered ETFs, it provides downside protection against returns along with upside capture of a portion of positive returns. I asked ChatGPT about FIAs, and it defines them as: “A type of annuity contract that offers a guaranteed minimum interest rate combined with the opportunity to earn additional interest based on the performance of a specific financial market index, such as the S&P 500.”
There are many forms of FIAs, but for this article I’m simplifying the analysis of our research:
- We used the S&P 500 index (without dividends reinvested) as the benchmark for market performance.
- We focused on the ability of the FIA to efficiently accumulate savings for subsequent distributions or exchanges to a lifetime annuity.
- We excluded the plethora of FIA riders that turn the product into its own mini plan for retirement income.
- We used a popular FIA formula that translates market performance to an FIA credited rate on a contract designed for accumulation and does that translation on a monthly basis.
Our results confirm that FIAs allow you to minimize (or avoid) much of the risk of down markets. They also confirm that an investor needs to hold the contract for longer periods. In other words, stay the course. The negative is that you may not fully benefit from a boom either.
How do you evaluate an FIA to help you manage risk?
For an investor, the challenge in analyzing the FIA is the age-old question: Compared to what? Is the FIA an alternative to a fixed-income portfolio, a balanced portfolio of stocks and bonds, a variable annuity with income protection, a buffered ETF? And of all the hundreds of FIA designs on the marketplace, which do you pick to analyze?
To start the process, we chose products designed for the efficient accumulation of retirement savings and no riders. Our stock market measure was the S&P 500 index. While looking at the last 30 years of investment results, we studied holding periods of 10 through 25 years and compared them to market returns of the S&P without dividends and Treasury yields.
We also evaluated the FIA in terms of the usual client benefits of (1) principal protection, (2) upside capture of market performance and (3) annuity tax benefits. I added one that is often missed but may be the most important: (4) stay the course.
Downside protection
Using our model, we looked at all 10-year periods (a 10-year hold is necessary to avoid surrender charges) and compared the FIA vs the S&P 500 over the same 10-year periods. You will see it beats the lows but doesn’t achieve the highs, just as it is designed to do.
Comparison of Returns Between FIA and S&P 500
Based on 10-year compound annual returns for 30 years ending 12-31-2023
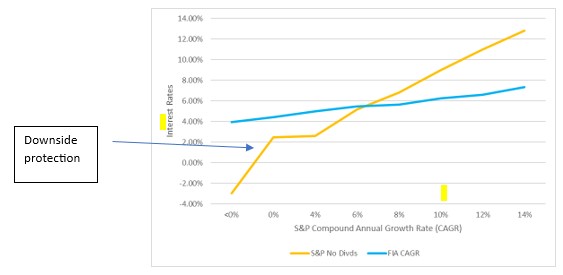
Our study assumes the FIA contract continues to use the same formula and terms through the life of the annuity.
Upside capture
You might wonder, while digesting that slow and steady rise in FIA value over a decade, whether it might just be easier to invest your money in reliable bonds. But our FIA outperformed the 10-year Treasuries during the same period most of the time.
Comparison of Returns Between FIA and 10-Year Treasury based on 10-year compound annual returns for 30 years ending 12-31-2023
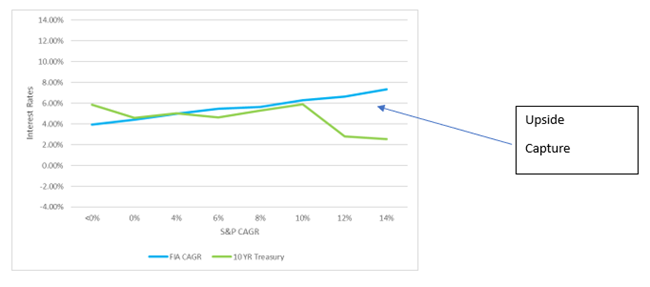
Conclusions
Having analyzed the product on an independent and stand-alone basis, how do you include it in your plan for retirement income? What percentage of savings? What does it replace in your current portfolio? How do you efficiently convert to secure income? What’s your planned holding period? How do you use its annuity tax benefits?
Looking ahead
Now that you know what an FIA offers, our next article will discuss more of the planning considerations, for example, pairing an FIA with a Go2Income plan for retirement income.
When you visit Go2Income to order your first plan or to make adjustments to an existing one, you will also be able to ask for a report on how an FIA might further enhance your retirement.